Insulated aluminum pcb entry board, also known as aluminum-based copper clad laminate, is a composite type composed of aluminum entry sheet (aluminum plate), insulating medium layer and copper foil. As a special type of PCB, has excellent heat dissipation performance, high mechanical strength and toughness, excellent dimensional stability, and good electromagnetic shielding. Due to these advantages of the insulated aluminum pcb entry board, it is widely used in high-power and high-heating component circuit boards, but the intermediate insulating dielectric layer (oxide film) is that after the aluminum entry sheet is anodized, a layer of wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant and electrically insulating oxide film, the quality of this film directly determines the quality of the aluminum entry sheet.
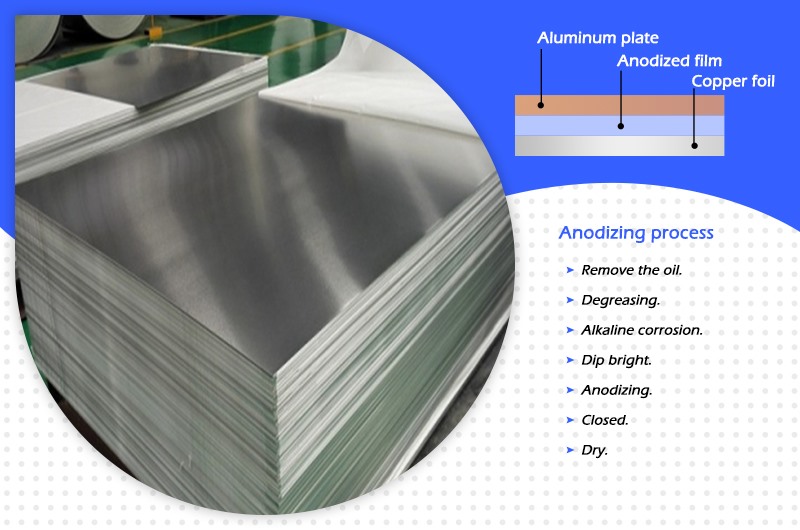
Anodizing process of insulated aluminum pcb entry board
The anodic oxide film (ie insulating dielectric layer) is the intermediate layer between the aluminum entry sheet and the copper foil.
(1) Remove the oil. The surface of the aluminum entry sheet is protected by an oil layer during processing and transportation. The oil layer must be cleaned before use. To remove the oil is to use gasoline as a solvent to dissolve it, and then use a water-soluble cleaning agent to remove the oil.
(2) Degreasing. In order to completely remove the grease, the board after degreasing can be directly soaked in concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, and then rinsed with clean water.
(3) Alkaline corrosion. The surface of the aluminum entry sheet should have a certain degree of roughness. Since aluminum and the aluminum oxide film layer on the surface are both amphoteric materials, the aluminum base material can be eroded by an acidic, alkaline or composite alkaline solution system to achieve the purpose of roughening.
(4) Dip bright. Since aluminum contains other impurity metals, some inorganic compounds will inevitably adhere to the surface of the substrate during the roughening process. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the inorganic compounds formed on the surface before electrolytic oxidation, and then formulate according to the analysis results. A suitable dipping solution is used, and finally the roughened aluminum substrate is immersed in this dipping solution for a period of time to ensure that the surface of the aluminum plate is clean and bright before anodizing.
(5) Anodizing. A layer of aluminum oxide film is formed on the surface of the aluminum plate by means of electrolysis, thereby improving the surface hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance and electrical insulation of the aluminum substrate, so as to be further dyed or primed with insulating impregnating paint.
(6) Closed. After the aluminum substrate is anodized, an oxide film is formed on its surface, but this film is porous and honeycomb-shaped. If the surface is not sealed, it will absorb a large amount of moisture, dust, gas and other impurities and affect the Heat resistance, solder dip resistance, breakdown strength, etc. of the substrate. Therefore, it is necessary to seal the conductive lines before finally forming them. It is to put the electro-oxidized aluminum substrate directly into a blocking solution or a low molecular weight insulating impregnating varnish for a few minutes.
(7) Dry. Drying is to bake the above-treated aluminum entry sheet in an oven to remove the water vapor remaining in the oxide layer for easy storage.

